EDC Oxychlorination Process
In the Oxychlorination process, EDC is formed by the highly exothermal reaction of ethylene with hydrogen chloride and oxygen.
Either air or oxygen can be used.
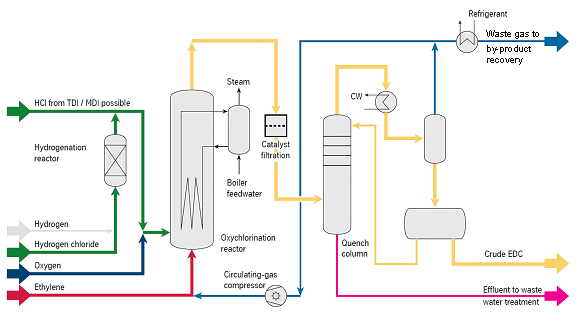
Oxychlorination – Oxygen-Lean-Process
The preferred way of Oxychlorination uses oxygen as an oxidizing agent. The catalyst bed is fluidized with circulating gas, the oxygen concentration is kept outside the flammable range (oxygen-lean operation). The very small off-gas stream of inerts and carbon oxides which are formed in the process is fed to the by-product revocery. The reaction mixture consisting of C2H4, HCl and O2 is catalytically converted in the reactor to EDC in a highly exothermal reaction at a temperature above 200 °C. The heat is dissipated via internal cooling coils and recovered to generate steam.
The advantages of the Vinnolit process can be summarized as follows:
- Fluidized-bed reactor with excellent reaction heat distribution: no hot spots, no catalyst stickiness
- Proven materials and reliable and simple equipment
- Reactor and cooling coils made of carbon steel
- Crude EDC purity: 99.6 %
- High conversion of C2H4 to EDC: 99.0 %
- Low catalyst consumption
- Removal of catalyst fines either by simple waste water treatment or by catalyst filtration
- High flexibility of the plant, wide range of load
- Production of 10 bar steam for distillation units possible
- High safety standard, O2 content <1 %
